栈,队列和链表是最基础的数据结构,它们出现在很多生活场景中,比如说堆起来的集装箱,排队坐过山车,人体蜈蚣(如果不知道就别去搜了,啦啦啦)
栈
简介
栈就像堆起来的集装箱,或者是一堆书,每次加入新的元素只能在旧的之上,每次移出元素只能拿出最新加入的,所以有“后进先出”的原则(后进去的元素先出来)。
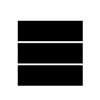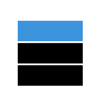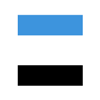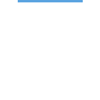
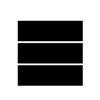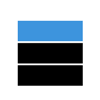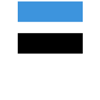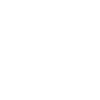
常见操作有:
| 进栈 | 出栈 |
|---|
 |  |
数组实现
一般我们用数组的第一个元素array[0]作为栈底,创建一个变量max_index来存储栈的最顶部元素在数组中的下标,也就是数组最后一个栈中元素的下标。
进栈:max_index += 1,然后在该下标插入进栈的元素
出栈:初始化在max_index下标的元素,max_index -= 1
链表实现
单向链表,用head记录栈头,每个元素都有next指向下一个元素,栈顶的next指向NULL,size纪录链表大小(栈的大小)。
进栈:让在栈顶(链表尾部)元素的next指向新的元素,新元素的next为null,size += 1
出栈:初始化栈顶(链表尾部)元素,移动到上一个元素,设置next为null, size -= 1
C++ STL - stack
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| #include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
/* 创建一个栈,名为stk,元素类型为int */
stack <int> stk;
/* 使一个元素进栈 */
stk.push(1); // 1
stk.push(2); // 1 2
/*
* cout << stk.push(3) << endl;
* 错误!! stk.push(3) 返回void类型
*/
/* top() 返回栈最顶部的元素,且不改变栈 */
cout << stk.top() << endl; // print out 2
stk.push(1);
/* 返回栈的大小,有多少元素 */
cout << stk.size() << endl; // print out 3
/* 使栈顶部的元素出栈,返回void类型 */
stk.pop();
stk.pop();
cout << stk.top() << endl; // print out 1
/* 查看栈是否为空,如果为空,返回真(1) */
cout << stk.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}
|
队列
简介
队列就像排队一样,在队尾加入新的元素,在队首出队。所以队列有着“先进先出”的原则。
常见操作有:
| 入队 | 出队 |
|---|
 |  |
链表实现
使用单向链表,用head记录队列头,每个元素都有next指向下一个元素,队尾元素的next指向NULL,size纪录队列的长度。
入队:在队尾(链表尾部)插入元素,即旧队尾的next指向新元素,新元素的next指向null,size += 1
出队:通过next移动到第二个元素,head指向第二个元素,初始化原队首(链表头部),size -= 1
C++ STL - queue
基本用法和栈相同,
信息
队列分别使用front和back来返回队首和队尾元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
queue<int> q;
q.push(1); // q: 1
q.push(2); // q: 1 2
cout << q.front() << endl; // 1
cout << q.back() << endl; // 2
q.push(3); // q: 1 2 3
cout << q.size() << endl; // 3
q.pop(); // q: 2 3
cout << q.front() << endl; // 2
cout << q.back() << endl; // 3
cout << q.empty() << endl; // 0
return 0;
}
|
### 优先队列
优先队列类似于队列,只不过每个元素都有一个优先级,出队的元素不一定是最先入队的元素,而是当前队列中优先级最高的元素。就像有人有VIP卡的可以走专属通道,有人可以插队一样,对每个元素来说并不公平,叹气。
在C++ STL中,如果把int作为优先队列的类型, 默认情况下如果是整数的优先队列,那整数越小,则优先级越低。如果想整数越大,优先级越低,可以用greater<int>, 完整声明std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int> q_name。如有其它需求,可自定义cmp函数来完成优先级的比较。
警告
优先队列取队首元素不再是用队列的front(),而是用top()。
链表
简介
链表像一个个回形针串起来的链子。链表有多种结构:单向链表,双向链表,循环链表等等。主要介绍单向链表,其他类型脑补脑补ok的。
常见操作有:

C++ struct 实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| #include<iostream>
struct Node {
int value;
Node *next;
};
int main() {
Node *root;
Node *cur;
/* 初始化链表 */
root = new Node;
root->value = 1;
root->next = NULL;
cur = root;
/* 在链表尾部加入节点 */
cur = cur->next;
cur = new Node;
cur->value = 2;
cur->next = NULL; // linked list: 1 2
/* 在节点中间 */
Node *second = new Node;
second->value = 3;
second->next = cur;
root->next = second; // linked list: 1 3 2
/* 知道数据,寻找节点 */
cur = root;
while (cur->value != 3) {
cur = cur->next;
}
std::cout << cur->value << std::endl; // 3
/* 遍历到链表尾部 */
while (cur->next != NULL) {
cur = cur->next;
}
std::cout << cur->value << std::endl; // 2
/* 删除节点 */
Node *last;
cur = root;
if (cur == NULL)
; // empty list
if (cur->value == 1) { // if we want to delete the first node
root = cur->next;
delete cur;
} else {
while (cur->value != 1 && cur->next != NULL) {
last = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur->value == 1) {
last->next = cur->next;
delete cur;
}
}
}
|